-
Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEX) in FPLC

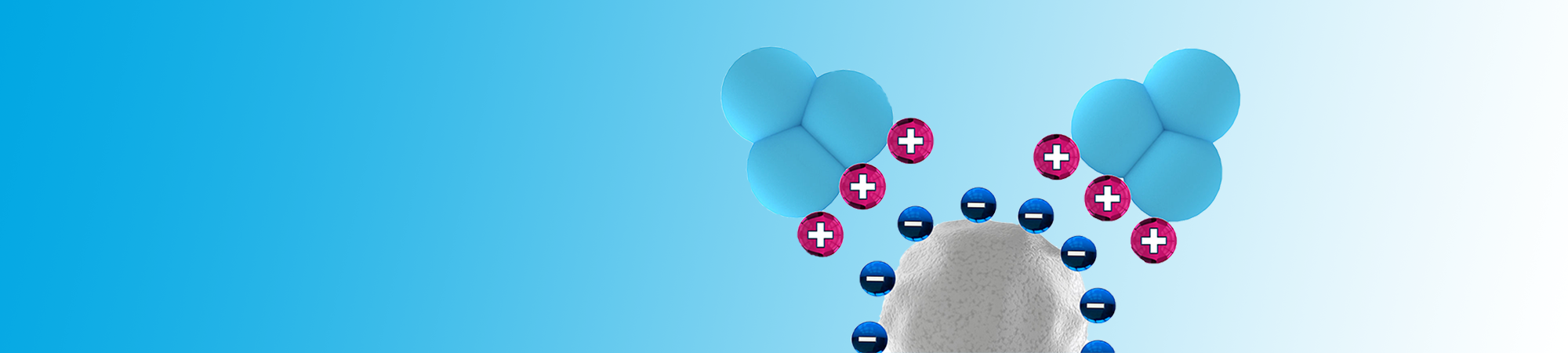
Ion exchange chromatography, abbreviated to IEX, is a popular technique in the protein purification pipeline. It is a unique chromatography technique that exploits the competitive binding of molecules in solution based on their relative binding to an ionic solid phase.
In this blog post, KNAUER explains the principles of ion exchange chromatography for FPLC applications in detail.
Introduction to Ion Exchange Chromatography
Ion exchange chromatography is used to separate proteins based on their charge. Different ion exchangers are used to exploit the adsorptive properties of charged proteins to a stationary phase with an opposing charge.
The first stage of ion exchange chromatography is equilibration with an appropriate buffer, the pH level of which affects the protein’s net charge. At a certain pH value, all charged molecules in solution carry a net charge close to zero. This is defined as their isoelectric point (pI). Generally speaking:
KNAUER is one of the leading European manufacturers and suppliers of anionic and cationic columns for ion exchange chromatography. With experience in the development of liquid chromatography solutions for a wide range of applications, we are uniquely equipped to help researchers and developers with their ion exchange chromatography needs. Contact us today to learn more.
From simple to complex, from Lab to Pilot scale: Design your AZURA® FPLC system according to your purification task. AZURA Bio Lab allows you to create FPLC systems with highest independence.

Acquiring pure proteins in good yields is important for many applications. However, manual protein purification is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process comprised of several purification steps. In this article, KNAUER explores some of the principles, systems, and processes of automated protein purification in more detail.