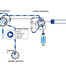
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are environmental pollutants and are widespread across the globe mainly due to long-term anthropogenic sources of pollution. Due to their high mutagenic and carcinogenic potential a sensitive determination is mandatory. The used system configuration makes it possible to switch between direct injection via autosampler and injection with an auxiliary pump (feed pump) without changing/replumbing the system. The use of autosampler injection or injection via feed pump enables the user to inject a broad variety of different volumes from μl to ml scale.

Exemplary structures of selected PAHs

Direct injection via autosampler of mixed standard, (1) fluoranthene, (2) benzo[b]fluoranthene, (3) benzo[k]fluoranthene, (4) benzo[a]pyrene, (5) benzo[g,h,i]perylene, (6) indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene

Direct injection on SPE via autosampler, (1) fluoranthene, (2) benzo[b] fluoranthene, (3) benzo[k]fluoranthene, (4) benzo[a]pyrene, (5) benzo[g,h,i] perylene, (6) indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene

Exemplary flow scheme for SPE load via sample/feed pump

Comparison of LOD values for direct injection (blue) and SPE injection (orange)
| Methode | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Modus | RP |
| Substanzen | EPA 610 PAH mixture, fluoranthene, benzo[b]fluoranthene, benzo[k]fluoranthene, benzo[a]pyrene, benzo[g,h,i]perylene, indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene |
| Schlüsselwörter | HPLC, online SPE, RP, PAH, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, solid phase extraction, multi-injection valve, EPA 610 |
| CAS Nummer | 206-44-0, 205-99-2, 207-08-9, 50-32-8, 191-24-2, 193-39-5 |
| Version | Version 1/ 11/2022 |

Wir helfen Ihnen gerne!